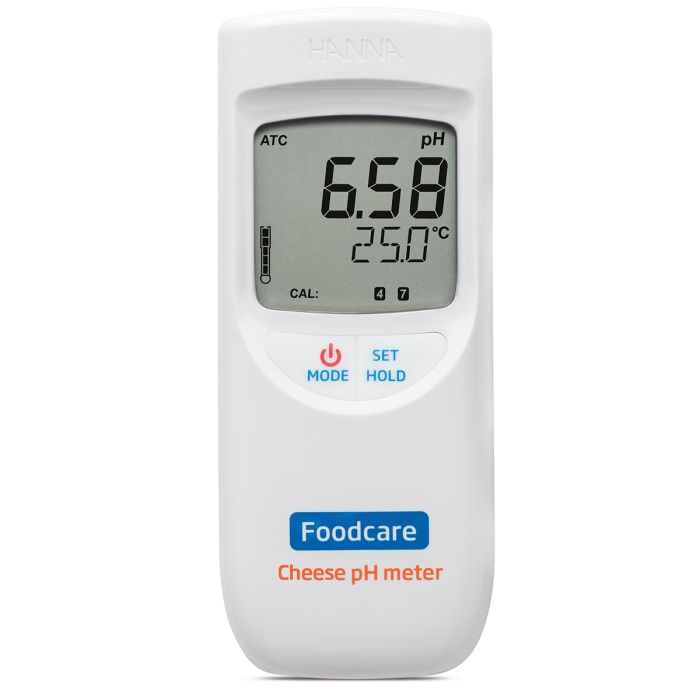
pH is an essential measurement throughout the entire cheesemaking process. From the initial measurements of incoming milk to the final measurements of ripened cheese, pH is the most important parameter for cheese quality and safety control.
Acidification of milk begins with the addition of bacterial culture and rennet. The bacteria consume lactose and create lactic acid as a byproduct of fermentation. The lactic acid produced will cause the pH of the milk to go down. Once the milk reaches a particular pH, the rennet is added. The enzymes in rennet help to speed up curdling and create a firmer substance. For cheesemakers that dilute their rennet, the pH of the dilution water is also critical; water that is near pH 7 or higher can deactivate the rennet, causing problems with coagulation.
Once the curds are cut, stirred, and cooked, the liquid whey must be drained. The pH of whey at draining directly affects the composition and texture of the final cheese product. Whey that has a relatively high pH contributes to higher levels of calcium and phosphate and results in a stronger curd. Typical pH levels at draining can vary depending on the type of cheese; for example, Swiss cheese is drained between pH 6.3 and 6.5 while Cheddar cheese is drained between pH 6.0 and 6.2.
During brining, the cheese soaks up salt from the brine solution and loses excess moisture. The pH of the brine solution should be close to the pH of the cheese, ensuring equilibrium of ions like calcium and hydrogen. If there is an imbalance during brining, the final product can have rind defects, discoloration, a weakened texture, and a shorter shelf life.